Addiction is a treatable disease.
The National Institute on Drug abuse (NIDA) states that “Addiction is a chronic disease characterized by drug seeking and use that is compulsive, or difficult to control, despite harmful consequences.”

Substance Misuse Disorder Facts
Use of alcohol, nicotine containing products, and illicit drugs remain high in modern American society. It is estimated that over half of the adult population use alcohol, nearly 1 in 10 smoke daily, and about 4% misuse opioids or have misused a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant in the form of cocaine or an amphetamine.
Over
140,000
Deaths annually in America due to AUD
27.6 Million
Adult Americans diagnosed with AUD in 2020
$249 Billion
Economic cost of AUD in 2020
Substance Misuse is Undertreated
Highlighting the need for more effective and better tolerated treatments only 362,000 (1.3%) of patients with Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) receiving treatment with a medication; only 16% received a drug to aid in their attempt to quit smoking; only 13% are treated with a medication who have opioid use disorder. There are no drugs approved for the treatment of cocaine or amphetamine use disorders.
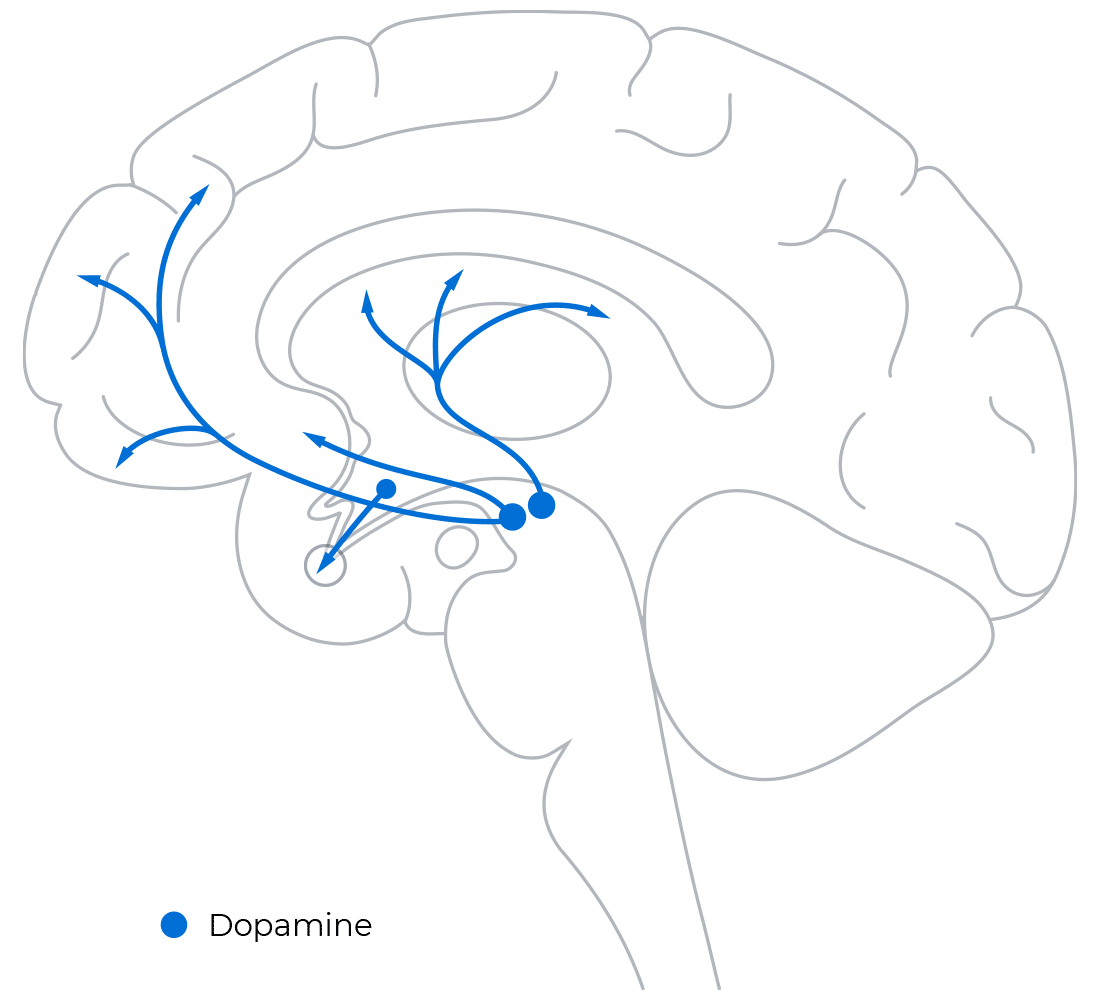
Neurochemical Pathways
A primary factor in the development of addiction is neurophysiologic reinforcement (reward). Evidence of at least one central reward-reinforcement pathway involving the neurotransmitter dopamine exists for drug self-administration in the human brain. This pathway involves dopaminergic neurons that originate in the ventral tegmental area and project into the nucleus accumbens and forebrain. Release of dopamine from these neurons onto the dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbens produces positive reinforcement and drives craving and addictive behavior.
Conditioned responses that trigger craving for addictive substances motivate drug-seeking behaviors often leading to heavy use. Indeed, strong cravings can persist long after drug use has stopped. Alcohol and other addictive agents stimulate an increase in dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens that mediates reward or reinforcement processes in brain.
ALDH2 inhibition is the key
ALDH2 inhibition restores normal dopamine levels by a use-dependent negative feedback mechanism.
Selective ALDH2 inhibition reduced self-administration of various addictive chemicals including alcohol, nicotine, cocaine, and opiates. Furthermore, ALDH2 inhibition reduces cue-reinstatement (craving relapse) of alcohol, cocaine, methamphetamine, and heroin and compulsive binge eating. These findings are important for the treatment of SUD given that SUD is commonly associated with, or co-dependent use, of other addictive substances or compulsive disorders. We also discovered that selective inhibition of ALDH2 can reduce anxiety. These results indicate that an orally bioavailable, selective, and reversible ALDH2 inhibitor may help patients reduce their use of addictive drugs and anxiety.
ALDH2 inhibition has shown to be effective in multiple models of Substance Use Disorders (SUD).
| Behavior Model | Result | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol Self Administration | Arolfo MP, Alcohol Clin Exp Res (2009) | |
| Alcohol Cue-Reinstatement / Relapse | Arolfo MP, Alcohol Clin Exp Res (2009) | |
| Nicotine Self Administration | Rezvani A, Journal of Drug & Alc Rsch (2015) | |
| Heroin Prime-Reinstatement / Relapse | Report on file | |
| Opiate Remifentanil Self Administration | Rezvani A, Journal of Drug & Alc Rsch (2015) | |
| Cocaine Self Administration | Martin M, Psychopharmacology (2021) Yao L, Nature Med (2010) |
|
| Cocaine Cue-Reinstatement / Relapse | Martin M, Psychopharmacology (2021) Yao L, Nature Med (2010) |
|
| Cocaine Prime-Reinstatement / Relapse | Yao L, Nature Med (2010) | |
| Methamphetamine Cue-Reinstatement / Relapse | Yao L, Nature Med (2010) | |
| Methamphetamine Locomotor and Biochemical Effects | Kim S, ACS Chem Neurochem (2021) | |
| Binge eating | Overstreet DH, Pharmacol Biochem Behav (2009) | |
| Anxiety | Overstreet DH, Pharmacol Biochem Behav (2009) |
Studies by ANS scientists and others provide validation of ANS technology.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021 Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Alcohol: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2020 Risk for Opioid Abuse is Diminished by Inhibiting AldehydeDehydrogenase-2 (ALDH-2) in Rats. Journal of Drug and Alcohol Research. 2019 Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 Anti-Sense in the Ventral Tegmental Area Reduces Alcohol Drinking. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 2019 From Ancient Chinese Medicine to a Novel Approach to Treat Cocaine Addiction. CNS & Neurological Disorders. 2015 Inhibition of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 (ALDH-2) Suppresses Nicotine Self-Administration in Rats. Journal of Drug and Alcohol Research. 2015 Behavioural Pharmacology. 2014 Nature Medicine. 2010 A selective ALDH-2 inhibitor reduces anxiety in rats. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 2009 Suppression of heavy drinking and alcohol seeking by a selective ALDH-2 inhibitor. Alcohol: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2009 Publications



